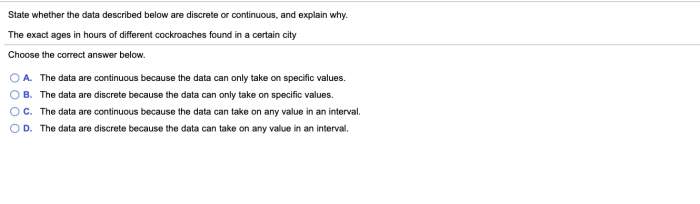
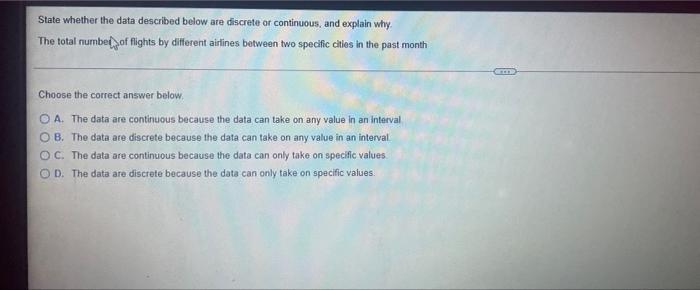
State whether the data described below are discrete or continuous sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
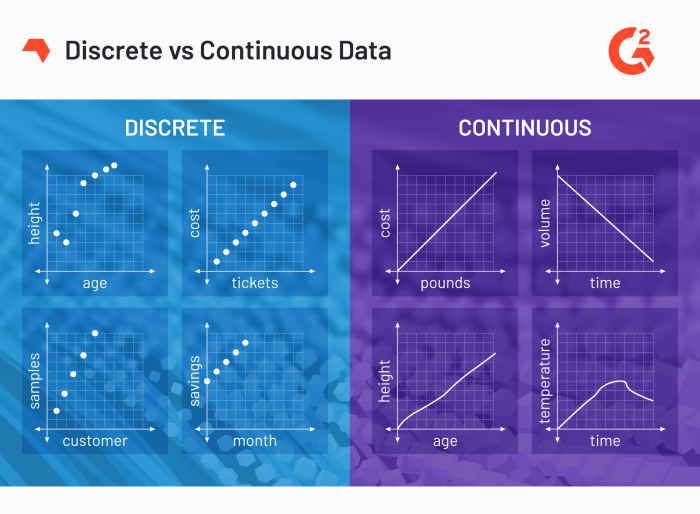
Discrete data, characterized by distinct and countable values, stands in contrast to continuous data, which flows seamlessly across a range of possibilities. Understanding the distinction between these two data types is crucial for effective data analysis and interpretation.
Discrete and Continuous Data
Data can be classified into two main types: discrete and continuous. Understanding the distinction between these two types is crucial for data analysis and statistical modeling.
Definitions and Explanations
Discrete data are data that can only take on certain, distinct values. They are often whole numbers or counts, and cannot be divided into smaller units.
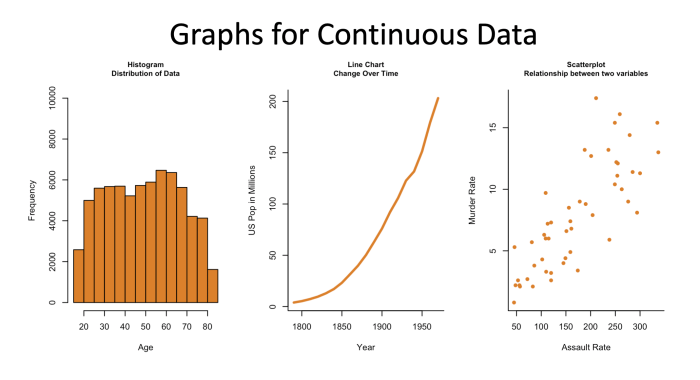
Continuous data, on the other hand, are data that can take on any value within a certain range. They can be divided into smaller and smaller units, and can be represented by real numbers.
Properties of Discrete and Continuous Data
Discrete data have the following key properties:
- They can only take on certain, distinct values.
- They are often whole numbers or counts.
- They cannot be divided into smaller units.
Continuous data have the following key properties:
- They can take on any value within a certain range.
- They can be divided into smaller and smaller units.
- They can be represented by real numbers.
Applications of Discrete and Continuous Data, State whether the data described below are discrete or continuous
Discrete data are commonly used in fields such as:
- Counting (e.g., number of people in a room)
- Categorical data (e.g., gender, race, education level)
- Probability distributions (e.g., binomial distribution, Poisson distribution)
Continuous data are commonly used in fields such as:
- Measurement (e.g., height, weight, temperature)
- Time series analysis (e.g., stock prices, economic data)
- Statistical distributions (e.g., normal distribution, t-distribution)
Examples and Illustrations
Here is a table with examples of discrete and continuous data:
| Discrete Data | Continuous Data |
|---|---|
| Number of students in a class | Height of students in a class |
| Number of cars in a parking lot | Temperature of a room |
| Number of defective products in a batch | Speed of a car |
Statistical Analysis of Discrete and Continuous Data
Discrete data are typically analyzed using statistical methods such as:
- Chi-square test
- Fisher’s exact test
- Binomial distribution
Continuous data are typically analyzed using statistical methods such as:
- t-test
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Normal distribution
FAQ Explained: State Whether The Data Described Below Are Discrete Or Continuous
What is the key difference between discrete and continuous data?
Discrete data takes on distinct values that can be counted, while continuous data can take on any value within a range.
Can continuous data be converted to discrete data?
Yes, continuous data can be discretized by dividing the range of values into intervals.
What are some examples of discrete data?
Number of children in a family, number of students in a class, number of defective products in a batch.
What are some examples of continuous data?
Height of a person, temperature of a room, weight of a car.