Embark on a comprehensive journey through the ATI Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test, a meticulously crafted assessment designed to evaluate your proficiency in calculating dosages for medications administered parenterally. This guide will provide an in-depth overview of the test, equipping you with the knowledge and strategies necessary to achieve success.
Delve into the fundamental concepts of dosage calculation, mastering units of measurement, conversion factors, and dimensional analysis. Explore the intricacies of parenteral medications, including routes of administration and factors influencing dosage and administration. Gain insights into common parenteral medications and their dosages, ensuring accurate and safe medication administration.
ATI Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test Overview
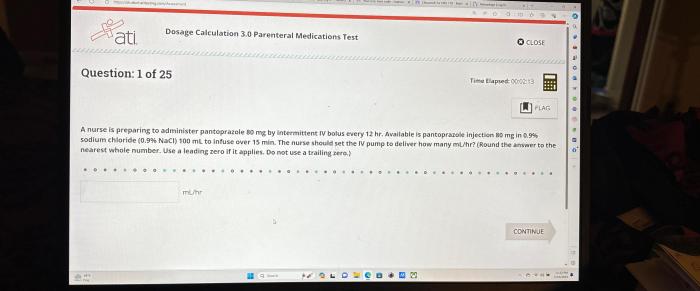
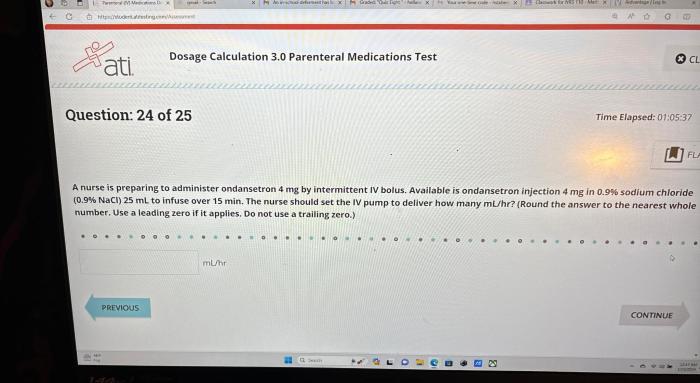
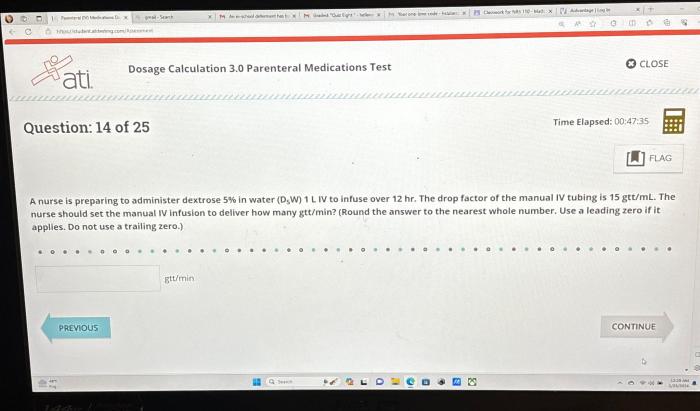
The ATI Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test is a standardized exam that assesses nurses’ ability to calculate and administer parenteral medications safely and accurately. It is designed for nurses who are working or planning to work in settings where parenteral medications are administered, such as hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
The test consists of 50 multiple-choice questions that cover a variety of topics related to dosage calculation and parenteral medications, including units of measurement, conversion factors, dimensional analysis, different routes of administration, and factors that affect the dosage and administration of parenteral medications.
Dosage Calculation Concepts
Dosage calculation is the process of determining the correct amount of medication to administer to a patient. The basic concepts of dosage calculation include units of measurement, conversion factors, and dimensional analysis.
- Units of measurement are the units used to express the amount of medication, such as milligrams (mg), grams (g), milliliters (mL), and liters (L).
- Conversion factors are the ratios used to convert from one unit of measurement to another, such as 1 g = 1000 mg or 1 mL = 1 cc.
- Dimensional analysis is a method of checking the accuracy of a dosage calculation by using the units of measurement to cancel out and ensure that the final answer is in the correct units.
There are two main methods used to calculate dosages: the ratio-proportion method and the formula method.
- The ratio-proportion method is a method of calculating dosages using proportions. In this method, the known ratio of the medication strength to the desired dose is used to calculate the unknown amount of medication to administer.
- The formula method is a method of calculating dosages using a formula. In this method, the formula for the medication is used to calculate the amount of medication to administer.
Parenteral Medications: Ati Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test
Parenteral medications are medications that are administered by injection. The different routes of administration for parenteral medications include:
- Intravenous (IV) injection: This route of administration involves injecting the medication directly into a vein.
- Intramuscular (IM) injection: This route of administration involves injecting the medication into a muscle.
- Subcutaneous (SC) injection: This route of administration involves injecting the medication into the fatty tissue beneath the skin.
- Intradermal (ID) injection: This route of administration involves injecting the medication into the layer of skin just beneath the epidermis.
The factors that affect the dosage and administration of parenteral medications include:
- The patient’s age, weight, and medical condition
- The type of medication being administered
- The route of administration
- The frequency of administration
Q&A
What is the purpose of the ATI Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test?
The ATI Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test assesses nurses’ ability to accurately calculate dosages for medications administered parenterally, ensuring patient safety and medication effectiveness.
What are the different types of questions on the ATI Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test?
The test includes various question types, such as multiple choice, fill-in-the-blank, and calculation problems, designed to evaluate your understanding of dosage calculation principles and your ability to apply them in real-world scenarios.
How can I prepare for the ATI Dosage Calculation 3.0 Parenteral Medications Test?
Effective preparation involves studying the test content, practicing dosage calculations, and utilizing study materials and practice questions. Additionally, implementing effective study habits and test-taking techniques can enhance your performance.