Indicate whether the following balanced equations involve oxidation reduction – Indicate whether the following balanced equations involve oxidation-reduction, delving into the fascinating realm of chemical reactions where electrons dance and atoms transform. Oxidation-reduction reactions, also known as redox reactions, play a crucial role in countless chemical processes, from the combustion of fuels to the functioning of batteries.
Join us as we explore the intricacies of these reactions, uncovering the secrets of electron transfer and the profound impact they have on our world.
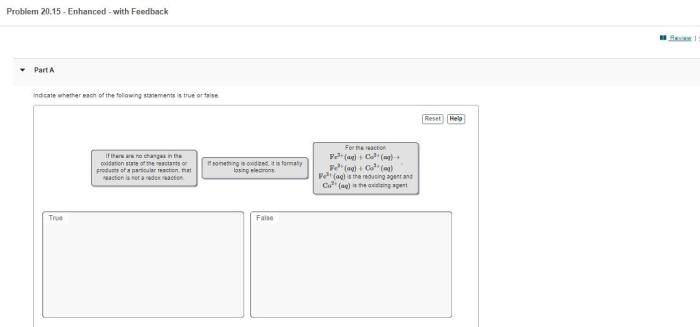
Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions, leading to changes in their oxidation states. Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons. Identifying oxidation-reduction reactions is essential for understanding their mechanisms and applications.
In this discourse, we will equip you with the knowledge and tools to determine whether a given balanced equation represents an oxidation-reduction reaction.
Balanced Equations and Oxidation-Reduction Reactions: Indicate Whether The Following Balanced Equations Involve Oxidation Reduction
Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions. In these reactions, one substance undergoes oxidation (loses electrons), while another substance undergoes reduction (gains electrons).
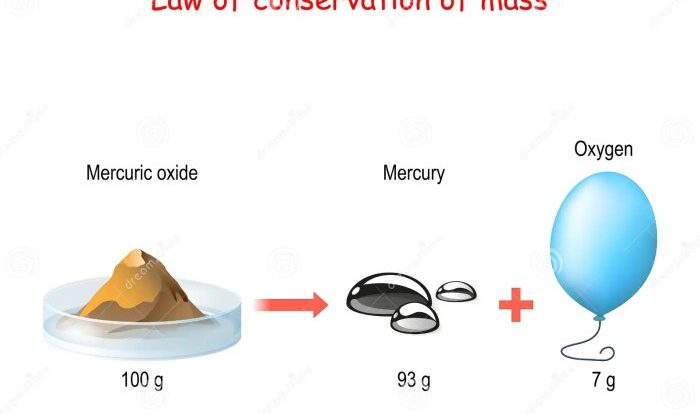
Balanced equations provide information about the reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction, as well as the stoichiometry of the reaction. By analyzing balanced equations, we can determine whether or not a reaction involves oxidation and reduction.
Identifying Oxidation and Reduction in Balanced Equations
To identify oxidation and reduction in balanced equations, we use oxidation numbers.
- Oxidation number is a numerical value assigned to each atom in a molecule or ion to indicate its oxidation state.
- An increase in oxidation number indicates oxidation, while a decrease indicates reduction.
Examples:
- In the reaction 2Na + Cl 2→ 2NaCl, sodium (Na) undergoes oxidation (oxidation number increases from 0 to +1), while chlorine (Cl) undergoes reduction (oxidation number decreases from 0 to -1).
- In the reaction 2Fe + 3Cl 2→ 2FeCl 3, iron (Fe) undergoes oxidation (oxidation number increases from 0 to +3), while chlorine (Cl) undergoes reduction (oxidation number decreases from 0 to -1).
The following table summarizes the rules for identifying oxidation-reduction reactions:
| Characteristic | Oxidation | Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation number change | Increase | Decrease |
| Electron transfer | Loss | Gain |
Types of Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Oxidation-reduction reactions can be classified into different types based on the nature of the reactants and products.
- Combustion reactionsinvolve the reaction of a substance with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light.
- Displacement reactionsinvolve the replacement of one element in a compound by another element.
- Disproportionation reactionsinvolve the simultaneous oxidation and reduction of the same element in a compound.
Examples:
- Combustion:CH 4+ 2O 2→ CO 2+ 2H 2O
- Displacement:Cu + 2AgNO 3→ Cu(NO 3) 2+ 2Ag
- Disproportionation:2Cu +→ Cu + Cu 2+
Balancing Oxidation-Reduction Equations, Indicate whether the following balanced equations involve oxidation reduction
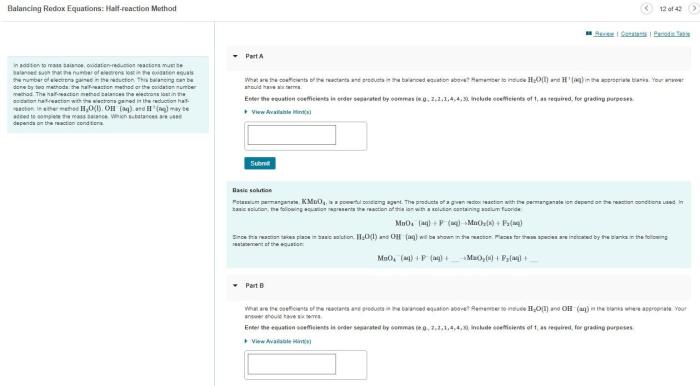
Balancing oxidation-reduction equations can be challenging due to the involvement of electron transfer.
The half-reaction method is a systematic approach to balancing oxidation-reduction equations.
- The overall reaction is divided into two half-reactions: one for oxidation and one for reduction.
- Each half-reaction is balanced separately in terms of mass and charge.
- The two half-reactions are then combined to form the overall balanced equation.
Examples:
- Unbalanced equation:Fe + Cu 2+→ Fe 2++ Cu
- Balanced half-reactions:
- Oxidation: Fe → Fe 2++ 2e –
- Reduction: Cu 2++ 2e –→ Cu
- Overall balanced equation:Fe + Cu 2+→ Fe 2++ Cu
Applications of Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Oxidation-reduction reactions play a crucial role in various aspects of our lives and industrial processes.
- Batteries:Oxidation-reduction reactions generate electricity in batteries, powering electronic devices.
- Fuel cells:Fuel cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy through oxidation-reduction reactions.
- Corrosion:Oxidation-reduction reactions can lead to the deterioration of metals, known as corrosion.
FAQ Overview
What are the key characteristics of oxidation-reduction reactions?
Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions, resulting in changes in their oxidation states. Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
How can I identify oxidation-reduction reactions based on balanced equations?
To identify oxidation-reduction reactions, look for changes in oxidation states of atoms or ions in the balanced equation. Oxidation is indicated by an increase in oxidation state, while reduction is indicated by a decrease in oxidation state.
What are some examples of oxidation-reduction reactions?
Combustion reactions, such as the burning of fuels, are examples of oxidation-reduction reactions. In these reactions, the fuel undergoes oxidation, while oxygen undergoes reduction.