Click on all the true statements about radiometric dating: an enthralling journey into the realm of time and matter, where the secrets of ancient materials are unraveled. This technique, a cornerstone of scientific inquiry, unveils the age of rocks, fossils, and artifacts, painting a vivid tapestry of Earth’s history.
Radiometric dating, a beacon of scientific precision, harnesses the power of radioactive decay to illuminate the passage of time. As radioactive isotopes disintegrate at predictable rates, they leave behind a trail of clues that scientists decipher to determine the age of materials.
1. Introduction: Click On All The True Statements About Radiometric Dating
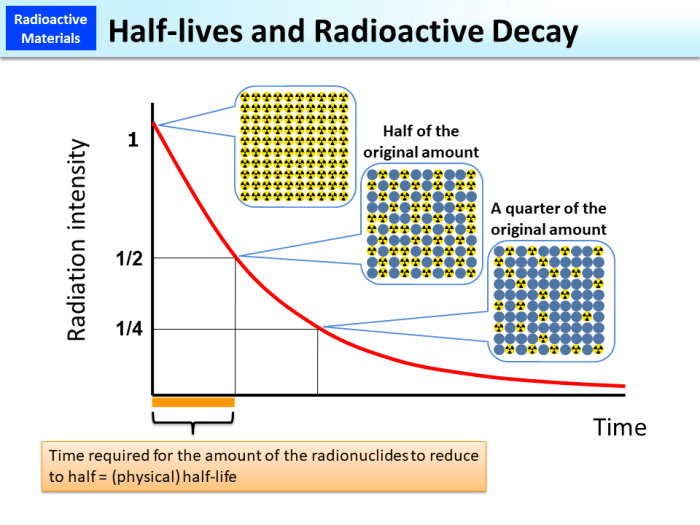
Radiometric dating is a scientific technique that utilizes the natural decay of radioactive isotopes to determine the age of materials. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including geology, archaeology, and paleontology, providing valuable insights into the age and evolution of Earth and its life forms.
The principles of radiometric dating are based on the concept of radioactive decay, where unstable isotopes undergo spontaneous transformations, emitting particles and energy. The rate of this decay is constant and can be measured, allowing scientists to calculate the time elapsed since the formation of the material.
2. Types of Radiometric Dating Methods
Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) Dating
K-Ar dating measures the decay of potassium-40 ( 40K) to argon-40 ( 40Ar). This method is widely used for dating rocks and minerals, especially volcanic rocks, as it provides reliable age estimates for materials up to several billion years old.
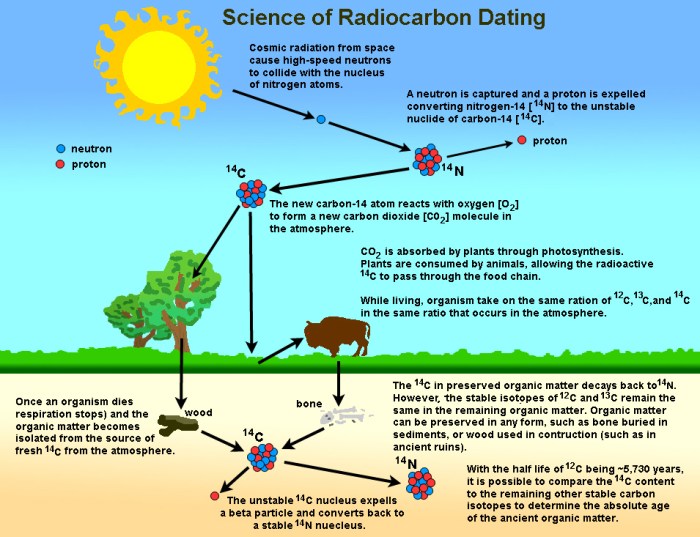
Carbon-14 (14C) Dating
14C dating is a technique specifically used for dating organic materials that are less than 50,000 years old. It measures the decay of radioactive carbon-14 ( 14C) to nitrogen-14 ( 14N). This method has revolutionized archaeology and paleontology, enabling scientists to date fossils, artifacts, and other organic remains with high precision.
Uranium-Lead (U-Pb) Dating
U-Pb dating involves measuring the decay of uranium-238 ( 238U) and uranium-235 ( 235U) to lead-206 ( 206Pb) and lead-207 ( 207Pb), respectively. This method is particularly useful for dating ancient rocks and minerals, including those found in the Earth’s crust and meteorites.
3. Applications of Radiometric Dating
Determining the Age of Geological Formations, Click on all the true statements about radiometric dating
Radiometric dating has enabled scientists to determine the age of geological formations, such as rock layers, mountain ranges, and ocean basins. By dating the minerals and fossils within these formations, researchers can reconstruct the Earth’s geological history and understand the processes that have shaped our planet over time.
Dating Fossils and Archaeological Artifacts
Radiometric dating has revolutionized the study of fossils and archaeological artifacts. It allows scientists to accurately date fossils, providing insights into the evolution of life on Earth. Similarly, it enables archaeologists to date artifacts, such as pottery, tools, and structures, helping to establish chronological sequences and understand past human civilizations.
4. Limitations and Uncertainties
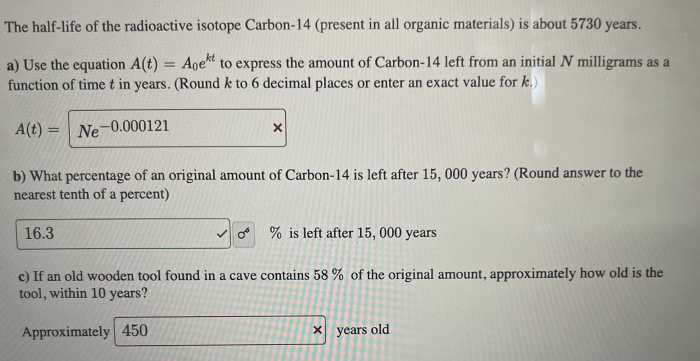
While radiometric dating is a powerful tool, it does have certain limitations and uncertainties. Factors such as contamination, alteration, and incomplete understanding of decay rates can affect the accuracy of the results.
Contamination can occur when the sample being dated is exposed to external sources of radioactive isotopes, potentially skewing the age estimate. Alteration, such as weathering or chemical reactions, can also affect the isotopic composition of the sample.
5. Historical Development
The development of radiometric dating techniques has been a gradual process marked by significant scientific advancements. The discovery of radioactivity by Henri Becquerel in 1896 laid the foundation for the field.
In 1905, Ernest Rutherford and Frederick Soddy proposed the concept of radioactive decay, which became the basis for radiometric dating. The first successful application of radiometric dating was conducted by Arthur Holmes in 1911, who used the lead-uranium method to date rocks.
6. Current Research and Future Directions
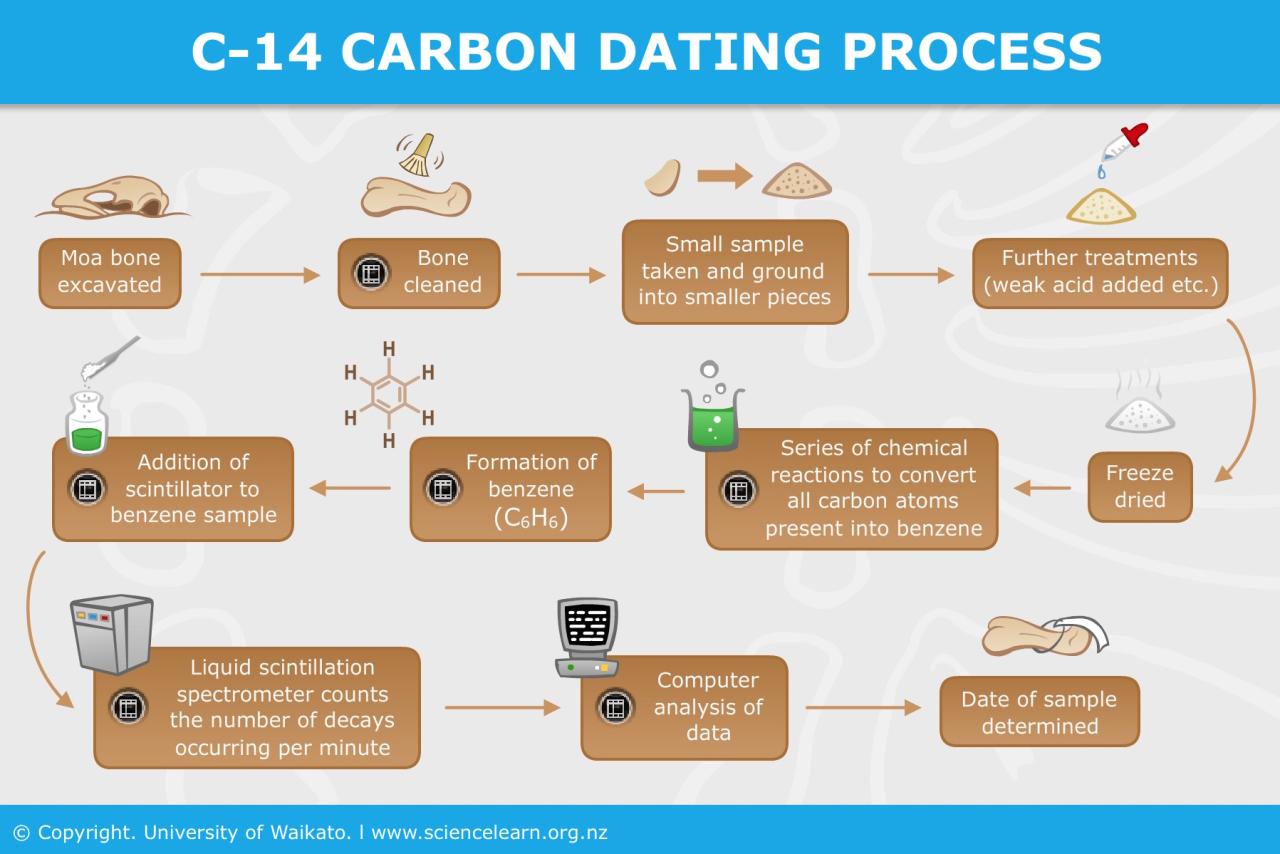
Radiometric dating techniques continue to evolve and improve, driven by advancements in instrumentation and analytical methods. Current research focuses on refining existing techniques and developing new methods for dating materials in challenging environments.
Future applications of radiometric dating include dating extraterrestrial materials, such as lunar and Martian samples, and exploring its potential in fields such as environmental science and climate change research.
FAQs
What is the fundamental principle behind radiometric dating?
Radiometric dating relies on the concept of radioactive decay, where unstable isotopes transform into more stable forms at a constant rate.
How does radiometric dating aid in understanding Earth’s history?
By determining the age of geological formations and fossils, radiometric dating provides crucial insights into the evolution of our planet and the timeline of past events.
What are some limitations associated with radiometric dating?
Factors such as contamination and alteration can potentially affect the accuracy of radiometric dating results, necessitating careful sample selection and interpretation.