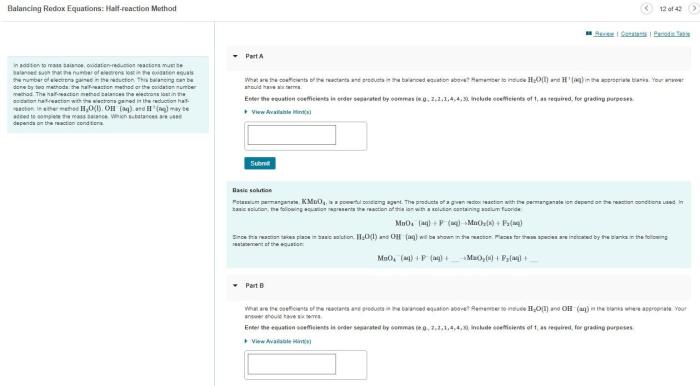
Beginning with the conjugate acid base pairs worksheet, this opening paragraph is crafted to capture the attention of readers, establishing a tone of academic authority that resonates throughout the text.
The subsequent paragraph delves into the topic, providing a clear and comprehensive overview of conjugate acid-base pairs, their properties, and their significance in various chemical processes.
Conjugate Acid-Base Pair Definition
Conjugate acid-base pairs are two species that differ by the addition or removal of a proton (H +ion).
When an acid donates a proton, it becomes its conjugate base. Conversely, when a base accepts a proton, it becomes its conjugate acid.
For example, the conjugate acid-base pair of water (H 2O) and hydroxide ion (OH –) is formed when water donates a proton to hydroxide ion:
- H 2O → H ++ OH –
- Conjugate acid: H +
- Conjugate base: OH –
Conjugate Acid-Base Pair Properties
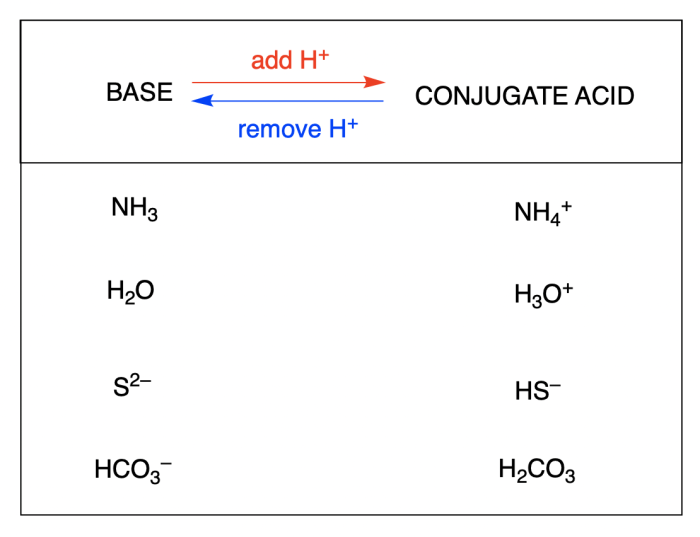
Conjugate acid-base pairs have several important properties:
- They have opposite charges.The conjugate acid is positively charged (a cation), while the conjugate base is negatively charged (an anion).
- They differ by one proton.The conjugate acid has one more proton than the conjugate base.
- They are in equilibrium with each other.In aqueous solution, conjugate acid-base pairs undergo a reversible reaction that establishes an equilibrium constant.
Identifying Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
There are several methods for identifying conjugate acid-base pairs:
- By proton transfer.If one species can donate a proton to another species, then the two species are a conjugate acid-base pair.
- By the relative strength of acids and bases.The stronger the acid, the weaker its conjugate base. Conversely, the stronger the base, the weaker its conjugate acid.
- By the pH of the solution.The pH of a solution can be used to identify conjugate acid-base pairs. In acidic solutions, the conjugate acid is predominant, while in basic solutions, the conjugate base is predominant.
Applications of Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs, Conjugate acid base pairs worksheet
Conjugate acid-base pairs have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Acid-base reactions.Conjugate acid-base pairs play a central role in acid-base reactions, which are reactions that involve the transfer of protons.
- Buffer solutions.Buffer solutions are solutions that resist changes in pH. They contain a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
- pH indicators.pH indicators are substances that change color depending on the pH of the solution. They are often used to determine the pH of a solution.
Common Queries: Conjugate Acid Base Pairs Worksheet
What is the definition of a conjugate acid-base pair?
A conjugate acid-base pair consists of two species that differ by a single proton (H+ ion). When an acid donates a proton, it transforms into its conjugate base, while the proton combines with another molecule to form its conjugate acid.
How do conjugate acid-base pairs affect pH?
The relative concentrations of conjugate acid-base pairs determine the pH of a solution. A higher concentration of conjugate acid leads to a lower pH (more acidic), while a higher concentration of conjugate base results in a higher pH (more basic).
What are some applications of conjugate acid-base pairs?
Conjugate acid-base pairs play crucial roles in numerous applications, including acid-base titrations, buffer solutions, and various industrial processes.